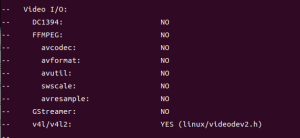
图像像素的算术操作是一种常见的操作方式,用于增强、融合、调整图像等。数据类型可以不一致,但是大小要一致。
像素算术操作的基本类型
主要包括以下几种算术操作:
- 加法操作
- 减法操作
- 乘法操作
- 除法操作
- 按位操作
- 其他非线性操作(如幂运算、对数运算等)
加法操作
(1) 使用 OpenCV 的 cv2.add()
cv2.add() 会对像素值进行 饱和运算(saturated operation),确保结果在 [0, 255] 范围内。
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 创建两张简单图像
image1 = np.ones((300, 300), dtype=np.uint8) * 120
image2 = np.ones((300, 300), dtype=np.uint8) * 140
# OpenCV 加法
result = cv2.add(image1, image2)
# 打印像素值
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 255(饱和处理)
cv2.imshow('Addition', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
(2) 使用 NumPy 加法
NumPy 的加法是 模运算,溢出的像素值会绕回。
result = image1 + image2
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 4((120 + 140) % 256)(3) 图片像素相加
def math_demo():
image = cv.imread('images/test.png')
if image is None:
print("Error: Image not found or failed to load.")
return
blank_copy = np.zeros_like(image)
blank_copy[:,:]=(50,50,50)
cv.imshow('image', image)
result = cv.add(image,blank_copy)
cv.imshow('blank_copy', blank_copy)
cv.imshow('result', result)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()![图片[1]-OpenCV-Python快速入门系列05图像像素的算术操作-天煜博客](https://blog.itianyu.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/20241123155205683-image-1024x527.png)
s
x
像素相加之后,图像变得更亮了,🤔如果想变暗是不是用减法就行了?
减法操作
(1) 使用 OpenCV 的 cv2.subtract()
cv2.subtract() 会对像素值进行饱和处理,确保结果在 [0, 255] 范围内。
result = cv2.subtract(image2, image1)
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 20
(2) 使用 NumPy 减法
NumPy 的减法是直接相减,如果结果为负,则会绕回(取模)。
result = image1 - image2
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 236((120 - 140) % 256)
图片像素相减
def math_demo():
image = cv.imread('images/test.png')
if image is None:
print("Error: Image not found or failed to load.")
return
blank_copy = np.zeros_like(image)
blank_copy[:,:]=(50,50,50)
cv.imshow('image', image)
result = cv.subtract(image,blank_copy)
cv.imshow('blank_copy', blank_copy)
cv.imshow('result', result)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()![图片[2]-OpenCV-Python快速入门系列05图像像素的算术操作-天煜博客](https://blog.itianyu.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/20241123160219845-image-1024x522.png)
很明显,和想象的一样,颜色变得暗了。
乘法操作
(1) 使用 OpenCV 的 cv2.multiply()
cv2.multiply() 用于计算像素的逐元素乘积,支持浮点和整型运算,结果会进行适当截断。
result = cv2.multiply(image1, 2) # 将 image1 的像素值乘以 2
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 240
(2) 使用 NumPy 乘法
result = image1 * 2
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 240(3)像素乘以2
def math_demo():
image = cv.imread('images/test.png')
if image is None:
print("Error: Image not found or failed to load.")
return
blank_copy = np.zeros_like(image)
blank_copy[:,:]=(2,2,2)
cv.imshow('image', image)
result = cv.multiply(image,blank_copy)
cv.imshow('blank_copy', blank_copy)
cv.imshow('result', result)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()![图片[3]-OpenCV-Python快速入门系列05图像像素的算术操作-天煜博客](https://blog.itianyu.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/20241123160744951-image-1024x524.png)
t
对比度提升了。
除法操作
(1) 使用 OpenCV 的 cv2.divide()
cv2.divide() 会对每个像素逐元素相除,支持浮点和整型运算。
image2 = np.ones((300, 300), dtype=np.uint8) * 50
result = cv2.divide(image1, image2)
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 2
(2) 使用 NumPy 除法
result = image1 / image2
print(result[0, 0]) # 输出 2.4(3)像素处以2
def math_demo():
image = cv.imread('images/test.png')
if image is None:
print("Error: Image not found or failed to load.")
return
blank_copy = np.zeros_like(image)
blank_copy[:,:]=(2,2,2)
cv.imshow('image', image)
result = cv.divide(image,blank_copy)
cv.imshow('blank_copy', blank_copy)
cv.imshow('result', result)
cv.waitKey()
cv.destroyAllWindows()![图片[4]-OpenCV-Python快速入门系列05图像像素的算术操作-天煜博客](https://blog.itianyu.cn/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/20241123160505591-image-1024x519.png)
(
对比度降低了。
按位操作
(1) 按位与 cv2.bitwise_and()
result = cv2.bitwise_and(image1, image2)
cv2.imshow('Bitwise AND', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
(2) 按位或 cv2.bitwise_or()
result = cv2.bitwise_or(image1, image2)
(3) 按位异或 cv2.bitwise_xor()
result = cv2.bitwise_xor(image1, image2)
(4) 按位取反 cv2.bitwise_not()
result = cv2.bitwise_not(image1)
图像融合
使用 cv2.addWeighted() 可以融合两张图像,按权重进行像素的加权平均。
# 加权融合公式:result = α * image1 + β * image2 + γ
result = cv2.addWeighted(image1, 0.7, image2, 0.3, 0) # α=0.7, β=0.3, γ=0
cv2.imshow('Weighted Addition', result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
非线性操作
(1) 幂运算
result = cv2.pow(image1, 2) # 像素值平方
(2) 对数运算
result = cv2.log(image1.astype(np.float32) + 1) # 避免 log(0)
(3) 开平方
result = cv2.sqrt(image1.astype(np.float32))
(4) 指数运算
result = cv2.exp(image1.astype(np.float32))© 版权声明
转载请注明出处,并标明原文链接。
本网站尊重知识产权,如有侵权,请及时联系我们删除。
本站所有原创内容仅用于学习和交流目的,未经作者和本站授权不得进行商业使用或盈利行为。
本网站尊重知识产权,如有侵权,请及时联系我们删除。
本站所有原创内容仅用于学习和交流目的,未经作者和本站授权不得进行商业使用或盈利行为。
THE END










暂无评论内容